- Business Process Management (BPM)Document Management System (DMS)Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)Business Continuity Management (BCM)Enterprise Architecture (EA)Business Process Management (BPM)Document Management System (DMS)
- Document Control Overview
- AI Content Creation & Improvement
- Policy & Procedure Management (SOP)
- AI Content Mining Parser
- Collaboration & Governance
- Data Migration & Integration
- Interfacing Offline App
 Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)
Electronic Quality Management System (QMS)- Quality Management System Overview
- Document Control & Records Management
- Audit & Accreditation Management
- Corrective & Preventative Action
- Quality Event (Non-conformity / Complaint/ Compliance)
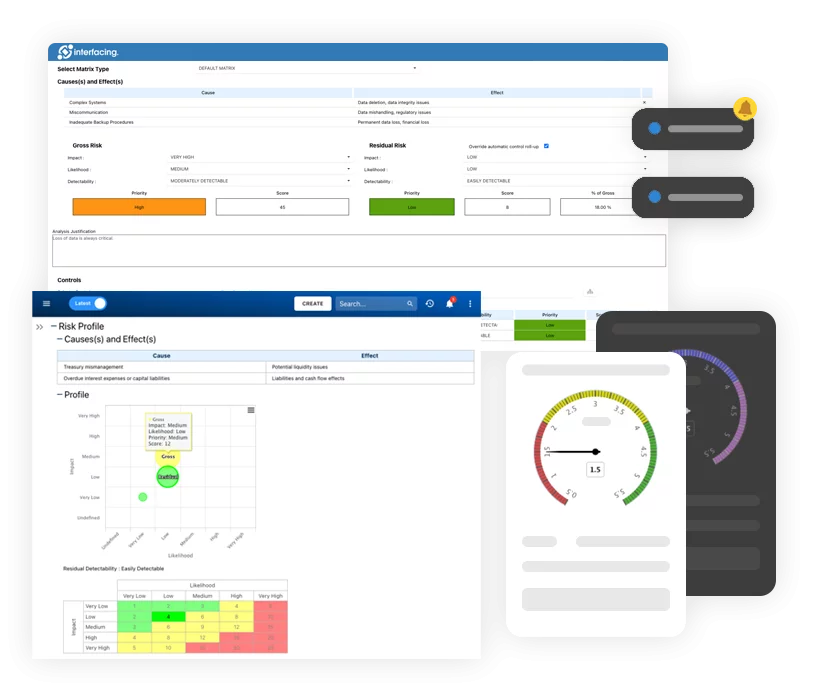
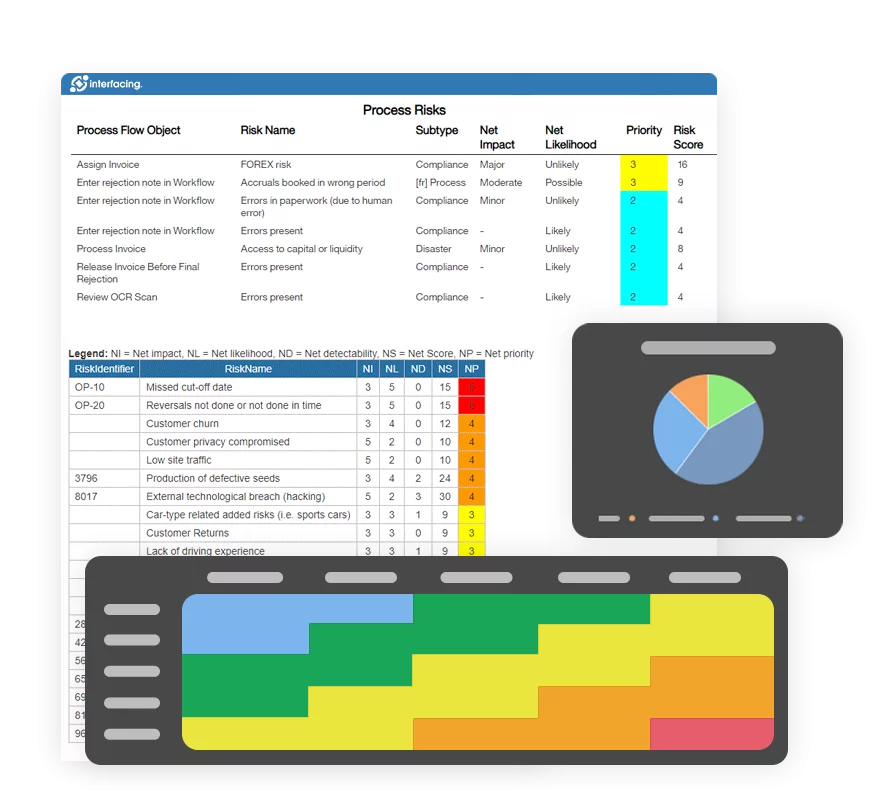
- Risk Management
- Incident Management
- Environmental Health & Safety
- Product & Supplier Management (SCAR)
- Training Management
- Control Management
- Action Items Management
- Management Review
- FMEA
- Pharmacovigilance
- Data Migration & Integration
 Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)
Risk, Governance & Compliance (GRC)- Risk, Governance & Compliance Overview
- Risk & Control Management
- Regulatory Compliance
- Collaboration & Governance
- Data Migration & Integration
- Interfacing Offline App
 Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)
Low Code Rapid Application Development (LC)- Low Code Automation Platform Overview
- Electronic Web Form Design (eFORMS)
- Database Table Entity Designer
- System Integration Designer
- Design & Manage Tasks
- Design & Manage BPMS Apps
- Custom Rules/Guards/Actions
- Electronic Services
- User Homepage
- BAM (Business Activity Monitoring)
- Custom Dashboard Design
- Data Migration & Integration
 Business Continuity Management (BCM)
Business Continuity Management (BCM)- Business Continuity Management Overview
- Business Impact Analysis
- Disaster Recovery Simulation
- Action Item Management
- Mass Notification Management
- Asset Management
- Interfacing Offline App
 Enterprise Architecture (EA)
Enterprise Architecture (EA) - IndustriesRegulatory ComplianceUse CasesLearning CenterFramework & PracticesIndustries
- Healthcare
- Medical Device Technology
- Life Science, Pharmaceutical
- Aerospace & Defense
- Airlines and Aviation
- Media & Telecommunications
- Government and Military
- Technology
- Energy
- Logistics & Port Operations
- Banking & Capital Markets
- Retail & Consumer
- Consulting
- Education
- Engineering & Construction
- Manufacturing
- Financial Services
- Insurance
- Chemicals
Regulatory Compliance- Regulatory Compliance
- ISO
- ISO 9001 (guide)
- ISO 9001:2026 (preparation)
- ISO 17025
- ISO 27000
- ISO 27001
- ISO27002
- ISO 42001
- EU AI Act
- SOC 2 Type 1 & 2
- Sarbanes Oxley
- GxP
- GRC
- Basel
- Digital Signature
- GDPR
- IFRS
- NIST SP 800-53
 Use Cases
Use Cases- Quality Management System (QMS)
- Digital Transformation
- Continuous Improvement
- Governance, Risk & Compliance
- Knowledge Management
- System Deployment (ERP, CRM…)
 Learning CenterFramework & Practices
Learning CenterFramework & Practices - AboutCustomer SuccessPartners


What is ISO 17025?
Please Select contact form.
A principal standard for all laboratories producing any testing or calibration results

ISO/IEC 17025 is a QMS (quality management system) and is the principal standard for all laboratories producing any testing or calibration results.
ISO/IEC 17025 defines the general requirements for competence in testing and calibration for all laboratories. For testing and calibration laboratories, this is the definitive ISO standard. On many occasions, regulatory authorities and suppliers will not accept test or calibration results from a lab that runs independent of any accreditation oversight. This is where ISO/IEC 17025 (originally known as ISO/ISO/IEC 17025 Guide 25) comes into play.
ISO/IEC 17025 was initially issued in 1999 by the International Organization for Standardization. This standard has quite a bit in common with ISO 9001 but it goes into greater detail and specificity when it comes to requirements for competency directly related to those organizations that use technical principles to produce testing and calibration results.
What is Meant by Accreditation?
In order to achieve full ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation, an officially authorized and accredited ISO/IEC 17025 third-party will thoroughly evaluate a laboratories quality management system and technical competency to perform all testing and calibrations involved. Accreditation of a laboratory means that it has successfully met both he Management and Technical Requirements of ISO/IEC 17025. The laboratory is now deemed technically competent to produce valid testing and calibration results.

Who is this standard for?
ISO/IEC 17025 benefits all organizations performing testing, sampling or calibration and requires reliable results that can then be validated. All types of laboratories are included here regardless of whether they are owned and operated by any government, industry or any other organization. This standard is very useful for research centers, universities regulators, governments, product certification organizations, inspection bodies and all other conformity assessment bodies that are required to do testing sampling or calibration.
Why was ISO/IEC 17025 revised?
Since its last publication in 2005, there have been significant changes to market conditions and technologies used. This newer version covers developments, vocabulary and technical changes in IT techniques. Additionally, this standard also takes into consideration the most recent version of ISO 9001.
What does ISO/IEC 17025:2017 look like?

Section 4: General Requirements – Impartiality and Confidentiality
Impartiality – Implies that the labs will not allow outside influence on the quality of test results. Examples of outside influences can be commercial, financial, governmental or any other agency having a gainful advantage to influencing test results in nature. This also accounts for any internal issues, personal influences, relationships or conflicts in general that would need to be addressed and resolved.
Confidentiality – the requirement here is that all information, including test results remain private.
Section 5: Structural Requirements – Organizational components of a laboratory
This section deals with a lab’s commitment to a professional functioning management system and its range of activities as an accredited laboratory. In order for a laboratory to receive accreditation, it can only be a standalone legal entity or a part of an existing legal entity, who would be responsible for the activities centered around the lab’s testing and calibration. Section 5 defines management’s responsibilities in the laboratory, and the responsibilities of management to regulatory authorities, organizations, and customers. Additionally, this section sets a basic overview requirement for personnel and what authority they would have and insight to the resources they require to perform their duties.
Section 6: Resource Requirements – the laboratory must have 6 clauses available
This section will address the six clauses mandated for a lab pertaining to personnel, equipment, support services, facilities, and systems required to carry out it’s lab activities.
Section 7: Process Requirements – 11 core processes to improve efficiency
A critical section, this one begins with: Review of Requests, Contracts and Tenders.
One of the most technical and important parts of Section 7 deals with Selection, Verification and Validation Methods. This section covers handling of test items, sampling and technical record keeping. The validity of results is vital here as is the control and quality monitoring in place at the laboratory. The requirements (and explanations) for testing proficiency is here along with several tools listed available for monitoring.
There is a great deal of detail in this standard related to results reporting. Requirements for dealing with non-conforming work and complaints are also listed here. This section was updated to reflect technologies impact on privacy in the Control of Data and Information Management sub-section.
Section 8: Management Systems Requirements – option A or B, eight activities, and internal audit
Option A – If a laboratory’s QMS (Quality Management System) runs independent of any other management system, it must comply with all Section 8 requirements of the ISO/IEC 17025 standard.
Option B – If the laboratory is part of a larger legal entity, or if it’s management system currently used is within compliance of ISO 9001:2015, then the Section 8 requirements would be met by the ISO 9001:2015 standard provided the labs activities are included and they can demonstrate fulfillment of this standard in compliance with ISO/IEC 17025 clauses 4 to 7.
Eight Activities – Included in this section are policies and their objectives, QMS documentation, addressing risks and opportunities, control of documentation, improvement, and corrective action.
Internal Audit – This gives general requirements for the internal audit and management review. Since it is only general input, compliance with ISO 19011 would be best used here to fill in the details (Guidelines for auditing management systems).
Why is it important to achieve accreditation?
Increasing customer confidence
Creating a proactive quality culture and risk-based business (not reactive)
Assurance in a laboratory’s credibility
Fostering an environment of pride and professionalism
To be accredited with ISO/IEC 17025 means that a laboratory has an acceptable quality management system in place. Additionally, it means that the laboratory has the competence and ability to provide attested testing and calibrations results. Labs that are accredited provide test results in accordance with ISO/IEC 17025 international standards that are mutually acceptable between different regulatory organizations and governmental bodies. Across all accreditation bodies, test results provided by any one lab will meet the same minimum standard regardless of lab location, owner or operator that has been accredited as well as if the test results had been performed at any other lab within the accreditation body.
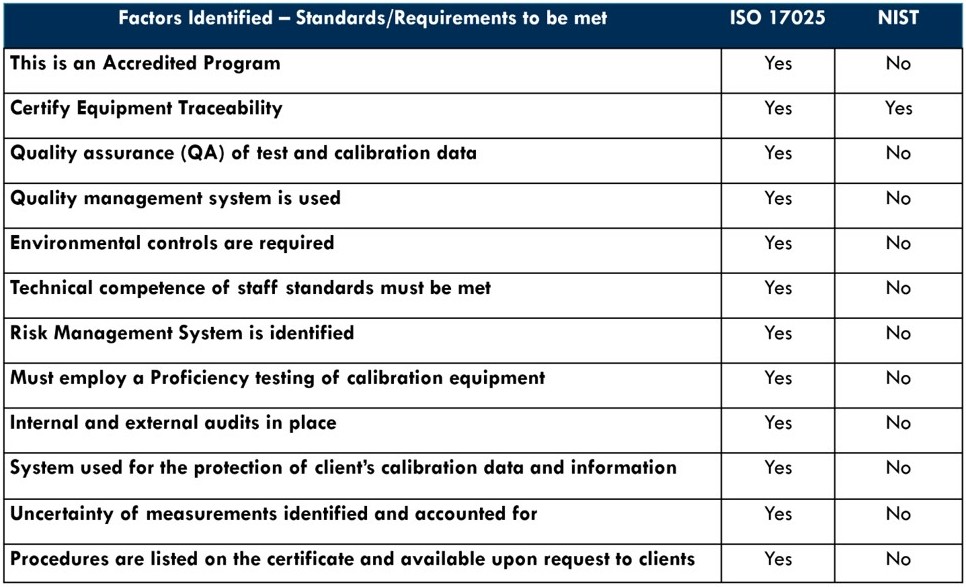
Comparing ISO/IEC 17025 to NIST
While there are commonalities between the National Institute for Standards and Technology (NIST) and ISO/IEC 17025, it is more important to note the differences as seen below that ISO/IEC 17025 identifies as critical to achieving accreditation.
How Interfacing Assists in Easing the Burden of ISO/IEC 17025 Documentation
With the growing complexity of managing ISO 17025 requirements, organizing information in a central location becomes increasingly important. When an auditor comes to site, they will assess management’s oversight of their third-party service providers as well as the company’s own controls. The majority of this oversight revolves mainly around documentation and the ability to review it. Proving this to an auditor means providing them with a record management system that can draw on the speed of access to the who, when and how’s of the organizations operations objectives.
Keeping this in mind is what Interfacing’s Integration Management System (IMS) documentation workflow automation is all about. Creating a safe, secure and protected data ecosystem is our commitment to your organization.

Summary
ISO/IEC 17025 is the best primary international standard when it comes to establishing laboratory competency and quality results. It also supports and fosters cooperation amongst testing laboratories and other bodies as a trusted source to provide wider acceptance between organizations and governments of verifiable and accurate results. Organizations in any country can accept test results and Certificates of Analysis (CoA) from accredited labs without the need for further testing, leading to better international trade of products and inform
Why Choose Interfacing?
With over two decades of AI, Quality, Process, and Compliance software expertise, Interfacing continues to be a leader in the industry. To-date, it has served over 500+ world-class enterprises and management consulting firms from all industries and sectors. We continue to provide digital, cloud & AI solutions that enable organizations to enhance, control and streamline their processes while easing the burden of regulatory compliance and quality management programs.
To explore further or discuss how Interfacing can assist your organization, please complete the form below.

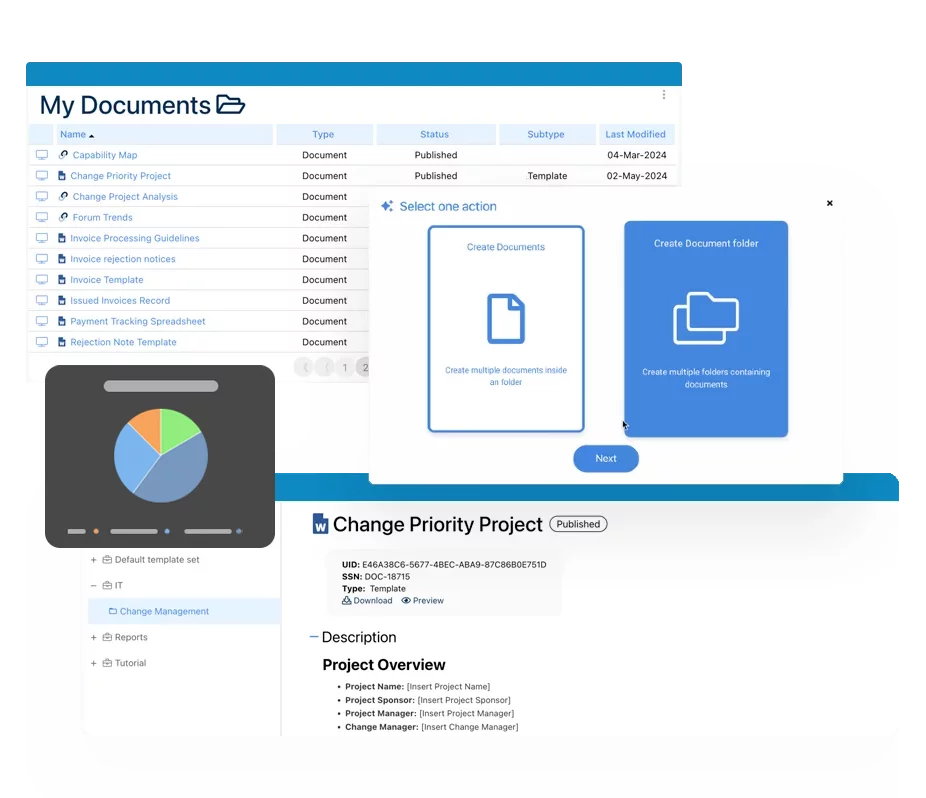
Documentation: Driving Transformation, Governance and Control
• Gain real-time, comprehensive insights into your operations.
• Improve governance, efficiency, and compliance.
• Ensure seamless alignment with regulatory standards.

eQMS: Automating Quality & Compliance Workflows & Reporting
• Simplify quality management with automated workflows and monitoring.
• Streamline CAPA, supplier audits, training and related workflows.
• Turn documentation into actionable insights for Quality 4.0

Low-Code Rapid Application Development: Accelerating Digital Transformation
• Build custom, scalable applications swiftly
• Reducing development time and cost
• Adapt faster and stay agile in the face of
evolving customer and business needs.
AI to Transform your Business!
The AI-powered tools are designed to streamline operations, enhance compliance, and drive sustainable growth. Check out how AI can:
• Respond to employee inquiries
• Transform videos into processes
• Assess regulatory impact & process improvements
• Generate forms, processes, risks, regulations, KPIs & more
• Parse regulatory standards into requirements

Request Free Demo
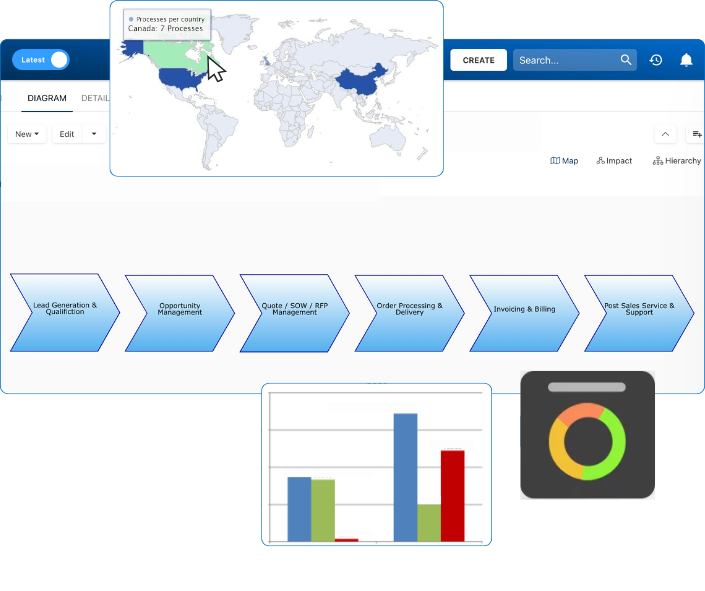
Document, analyze, improve, digitize and monitor your business processes, risks, regulatory requirements and performance indicators within Interfacing’s Digital Twin integrated management system the Enterprise Process Center®!
Trusted by Customers Worldwide!
More than 400+ world-class enterprises and management consulting firms