Corrective Action Preventive Action (CAPA)
Definition and Use
Corrective Action Preventive Action (CAPA) is the process used to examine and solve problems, identify causes, and takes any corrective actions, all in order to prevent any recurrences of the root cause(s). It’s goal is to remove any causes of non-conformities (any deviation from a set standard) or any other undesirable outcome to a process. Examples of non-conformance include customer or market complaints, machinery or design failures, faulty QMS in place or a misinterpretation of written instructions to carry out work details. CAPA is implemented to provide continued observation in order to maintain the standards (including regulatory requirements) put in place to eliminate recurrence of an identified instance of failure.
Ultimately, CAPA’s primary objective is to ensure the problem will no longer surface again. CAPA is applied in a variety of industry verticals, not the least of which include:
- Product Design
- Use-Applications
- Testing, Verification and Validation
- Manufacturing
- Shipping, Distribution, Packaging, and Transport

What is CAPA?
CAPA is the output of the US FDA requirement known as FDA 21 CFR 820.100. This is a requirement that was specific to medical device manufacturers and must be included in their QMS (Quality Management System).
CAPA is broken down into two related but very distinct functions:
CA (Corrective Action)
This is an extension of RCA (Root Cause Analysis). Its first goal is to find the base event, root cause or error that preceded the problem. Taking action directly related to the root cause or error is the second goal.
PA (Preventive Action)
This is similar to Read Across / Lessons Learned. PA’s primary goal is to notify an agency or organization of the root cause and prevent the problem from recurring or returning in all other facilities lines or products.
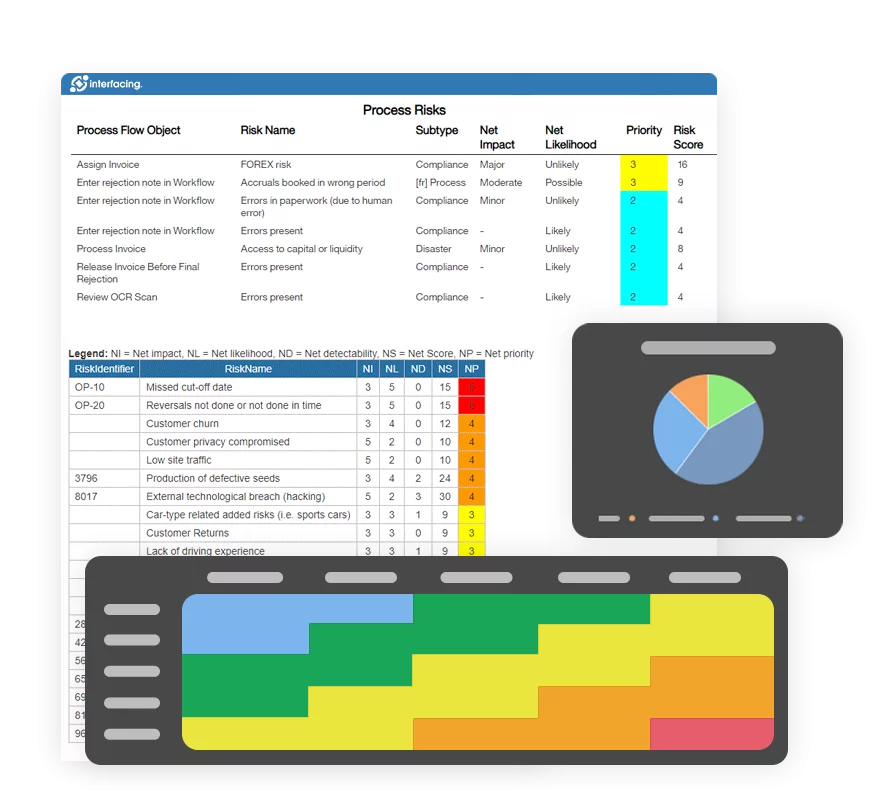
Verify that CAPA system procedure(s) that address the requirements of the quality system regulation have been defined and documented.
Determine if appropriate sources of product and quality problems have been identified. Confirm that data from these sources are analyzed to identify existing product and quality problems that may require corrective action.
Determine if sources of product and quality information that may show unfavorable trends have been identified. Confirm that data from these sources are analyzed to identify potential product and quality problems that may require preventive action.
Challenge the quality data information system. Verify that the data received by the CAPA system are complete, accurate and timely.
Verify that appropriate statistical methods are employed (where necessary) to detect recurring quality problems. Determine if results of analyses are compared across different data sources to identify and develop the extent of product and quality problems.
Determine if failure investigation procedures are followed. Determine if the degree to which a quality problem or nonconforming product is investigated is commensurate with the significance and risk of the nonconformity. Determine if failure investigations are conducted to determine root cause (where possible). Verify that there is control for preventing distribution of nonconforming product
Determine if appropriate actions have been taken for significant product and quality problems identified from data sources.
Determine if corrective and preventive actions were effective and verified or validated prior to implementation. Confirm that corrective and preventive actions do not adversely affect the finished device.
Verify that corrective and preventive actions for product and quality problems were implemented and documented.
Determine if information regarding nonconforming product and quality problems and corrective and preventive actions has been properly disseminated, including dissemination for management revie
Key Phases with CAPA Use
CAPA is an excellent tool used for companies to identify defects or faults in a process (physical or digital). It is designed to effectively resolve and prevent them from recurrence.
There are a few key phases that a good CAPA system consists of:

- CAR: Corrective Action Request
This is the activity of originating a Corrective Action
- PAR: Preventative Action Request
PARs are used when conducting an investigation to find the root cause(s) of a potential problem in order to eliminate recurrence.
- NCR: Non-Conformist Request
NCRs refer to an instance when a product has been identified as not meeting its intended standards/specifications. This is regardless of whether the defect is minor or major. These non-conforming products must be logged and tracked as an occurrence either in paper or electronic form.
- SCAR: Supplier Corrective Action request
This is a formal request to a Supplier that asks them to correct a problem and explain in detail what will be done to ensure the problem is resolved to eliminate recurrence.
- CPAR: Corrective Preventative Action Request
CPARs are not commonly used as they tend to raise confusion. They are a combination of CAPA with an additional Request at the end.
- NCN: Non-Conformity Note
Originally initiated by Certification Bodies (Registrars) who issue Non-conformity notes with their audit reports. For clarity, NCRs are used to track product non-conformities, while NCNs are used to audit non-conformities.
- CIP: Continuous Improvement Program
- Identification of a problem and initiation of CAPA as a result.
Documenting the problem and describing it in as much detail as possible is the first step.
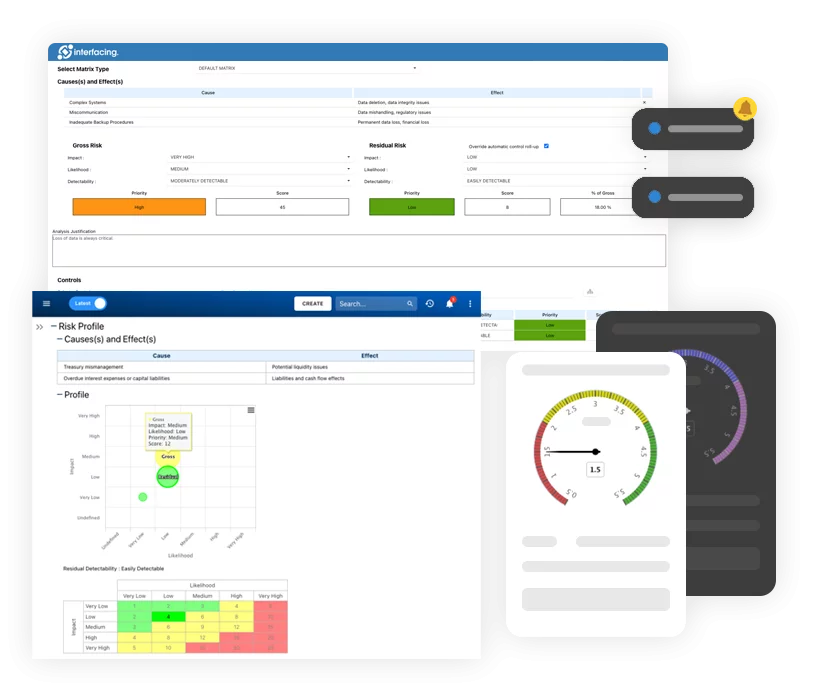
- Perform a Risk Analysis
Identifying the severity of the problem will help determine the resolution timeline to remediate.
- RCA (Root Cause Analysis
Identification of the non-conformity will be determined here.
- Implementation of CA and PA
This is where organizations will resolve the problem and ensure proper measures are implemented to prevent future recurrence.
- Verification
Both the implementation and effectiveness of the resolution will need to be verified as a permanent working solution to the original problem. If analysis shows unconformities, the organization will need to design a new solution.
- Closure
Once verification is complete, the CAPA process is determined to be closed.

Final Thoughts
Proper QMS will need CAPA implementation to readily identify and overcome nonconformities essential to operating a zero-defect-target organization.
Using a digital platform solution for your QMS / CAPA implementation can help with all tracking and audit trail requirements for the FDA’s, GMP, GCP (Good Clinical Practice) and GLP (Good Laboratory Practice). With a strong web-based application, access to a central repository for authorized users can be managed easily when accessing all documentation and information required to perform their specific tasks. CAPA’s requirements are met regarding online automated workflows to facilitate notifications, routing, e-approvals etc., not to mention the wide variety of analytics available.
Why Choose Interfacing?
With over two decades of AI, Quality, Process, and Compliance software expertise, Interfacing continues to be a leader in the industry. To-date, it has served over 500+ world-class enterprises and management consulting firms from all industries and sectors. We continue to provide digital, cloud & AI solutions that enable organizations to enhance, control and streamline their processes while easing the burden of regulatory compliance and quality management programs.
To explore further or discuss how Interfacing can assist your organization, please complete the form below.

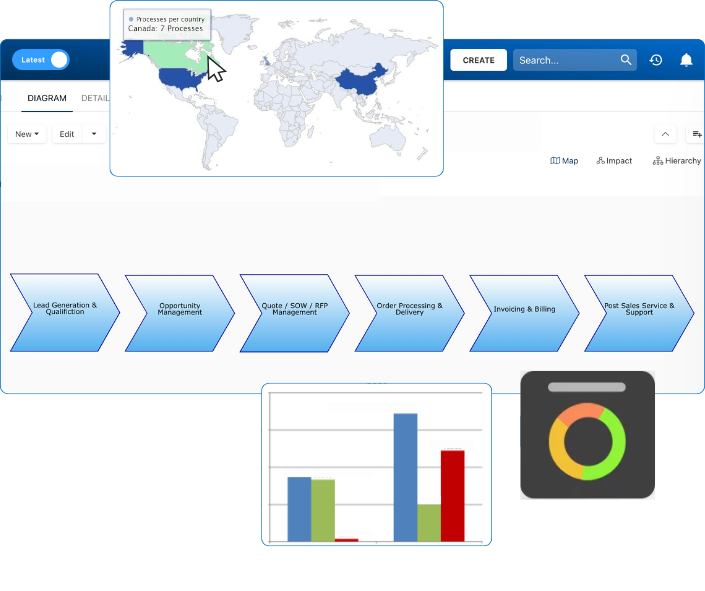
Documentation: Driving Transformation, Governance and Control
• Gain real-time, comprehensive insights into your operations.
• Improve governance, efficiency, and compliance.
• Ensure seamless alignment with regulatory standards.

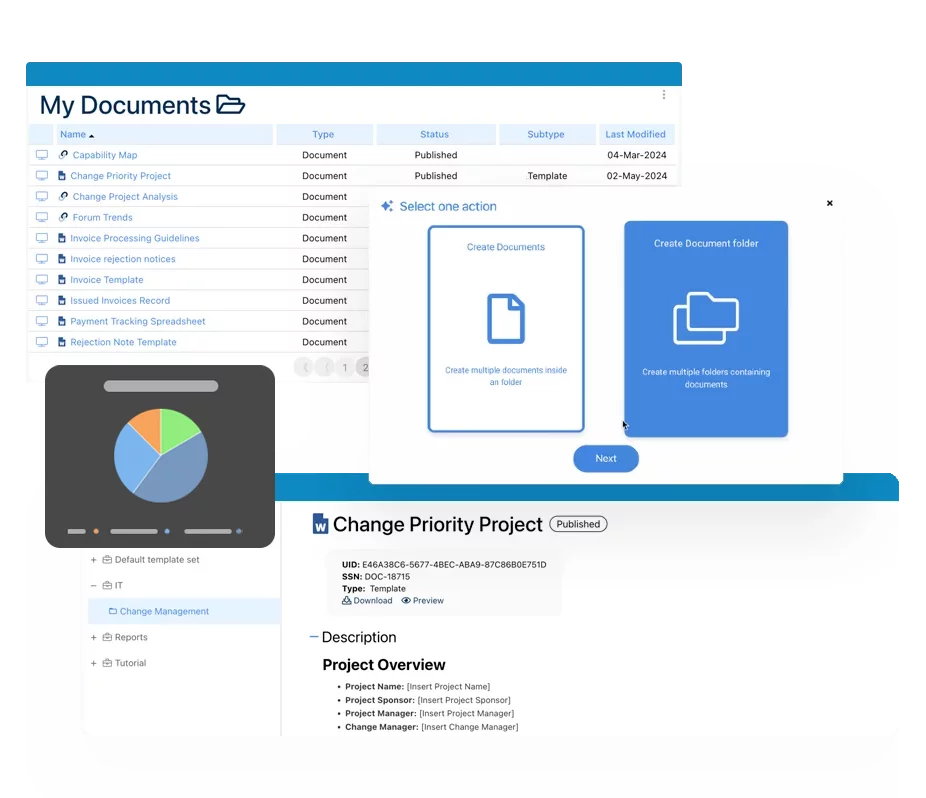
eQMS: Automating Quality & Compliance Workflows & Reporting
• Simplify quality management with automated workflows and monitoring.
• Streamline CAPA, supplier audits, training and related workflows.
• Turn documentation into actionable insights for Quality 4.0

Low-Code Rapid Application Development: Accelerating Digital Transformation
• Build custom, scalable applications swiftly
• Reducing development time and cost
• Adapt faster and stay agile in the face of
evolving customer and business needs.
AI to Transform your Business!
The AI-powered tools are designed to streamline operations, enhance compliance, and drive sustainable growth. Check out how AI can:
• Respond to employee inquiries
• Transform videos into processes
• Assess regulatory impact & process improvements
• Generate forms, processes, risks, regulations, KPIs & more
• Parse regulatory standards into requirements

Request Free Demo
Document, analyze, improve, digitize and monitor your business processes, risks, regulatory requirements and performance indicators within Interfacing’s Digital Twin integrated management system the Enterprise Process Center®!
Trusted by Customers Worldwide!
More than 400+ world-class enterprises and management consulting firms